Working with a laser rangefinder
TIP
Documentation for the image, versions, starting with 0.20. For older versions refer to documentation for version 0.19.
VL53L1X Rangefinder
The rangefinder model recommended for Clover is STM VL53L1X. This rangefinder can measure distances from 0 to 4 m while ensuring high measurement accuracy.
The image for Raspberry Pi contains pre-installed corresponding ROS driver.
Connecting to Raspberry Pi
TIP
Before using the rangefinder, please remove the protective film from it.
Connect the rangefinder to the 3V, GND, SCL and SDA pins via the I²C interface:
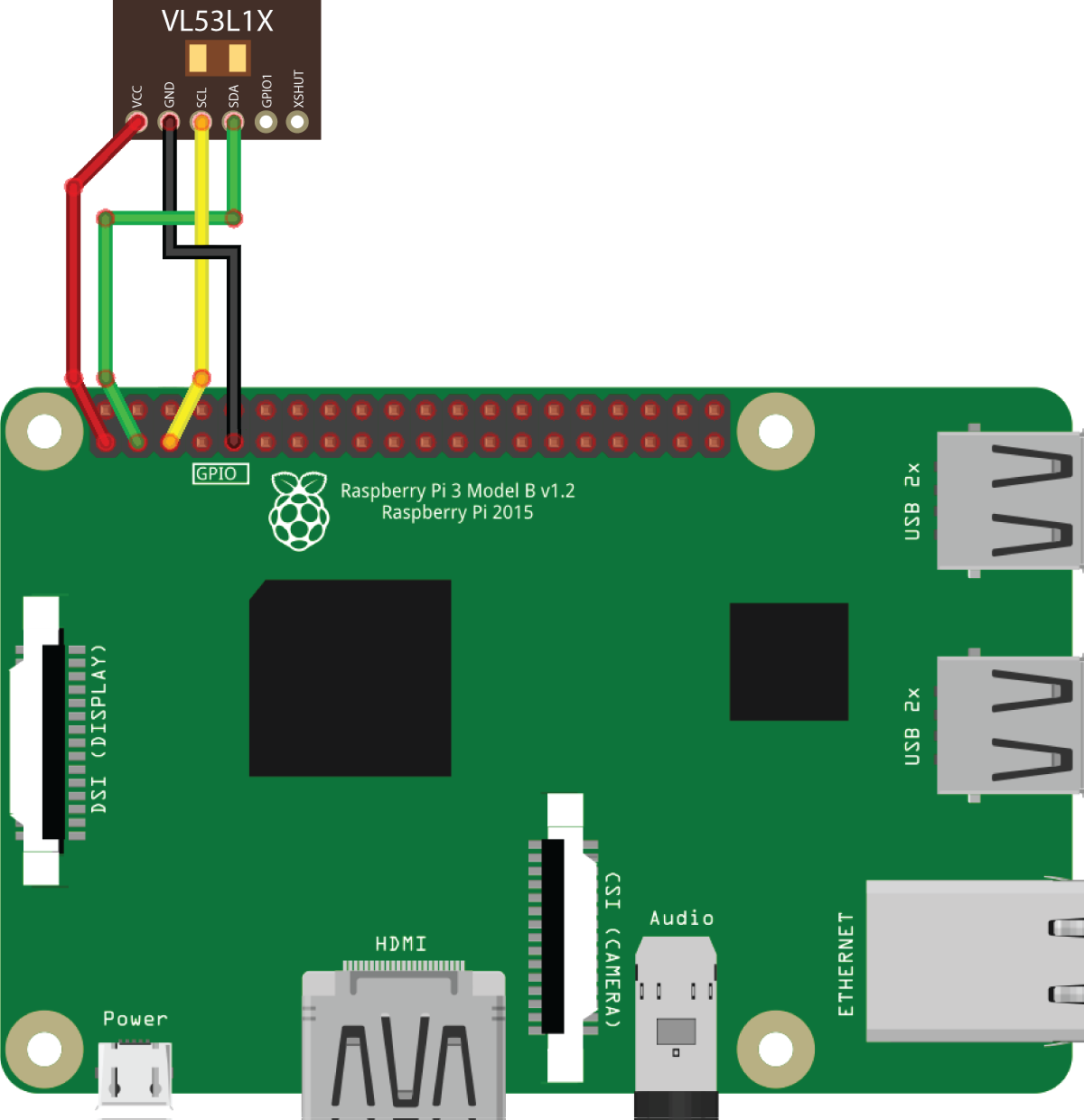
If the pin marked GND is occupied, you can use any other ground pin (look at the pinout for reference).
TIP
You can connect several peripheral devices via the I²C interface simultaneously. Use a parallel connection for that.
Enabling the rangefinder
Connect via SSH and edit file ~/catkin_ws/src/clover/clover/launch/clover.launch so that the VL53L1X driver is enabled:
<arg name="rangefinder_vl53l1x" default="true"/>
By default, the rangefinder driver sends the data to Pixhawk via the /rangefinder/range topic. To view data from the topic, use the following command:
rostopic echo /rangefinder/range
PX4 settings
TIP
We recommend using our custom PX4 firmware for Clover for best laser rangefinder support.
PX4 should be properly configured to use the rangefinder data.
Set the following parameters when EKF2 is used (SYS_MC_EST_GROUP = ekf2):
EKF2_HGT_MODE=2(Range sensor) – for flights over horizontal floor;EKF2_RNG_AID=1(Range aid enabled) – in other cases.
Set the following parameters when LPE is used (SYS_MC_EST_GROUP = local_position_estimator, attitude_estimator_q):
- The "pub agl as lpos down" flag should be set in the
LPE_FUSIONparameter – for flights over horizontal floor.
Receiving data in Python
In order to receive data from the topic, create a subscriber:
import rospy
from sensor_msgs.msg import Range
rospy.init_node('flight')
def range_callback(msg):
# Process data from the rangefinder
print('Rangefinder distance:', msg.range)
rospy.Subscriber('rangefinder/range', Range, range_callback)
rospy.spin()
Also it's possible to read one rangefinder measurement at a time:
from sensor_msgs.msg import Range
# ...
dist = rospy.wait_for_message('rangefinder/range', Range).range
Data visualization
You may use rqt_multiplot tool to plot rangefinder data.
rviz may be used for data visualization. To do this, add a topic of the sensor_msgs/Range type to visualization:
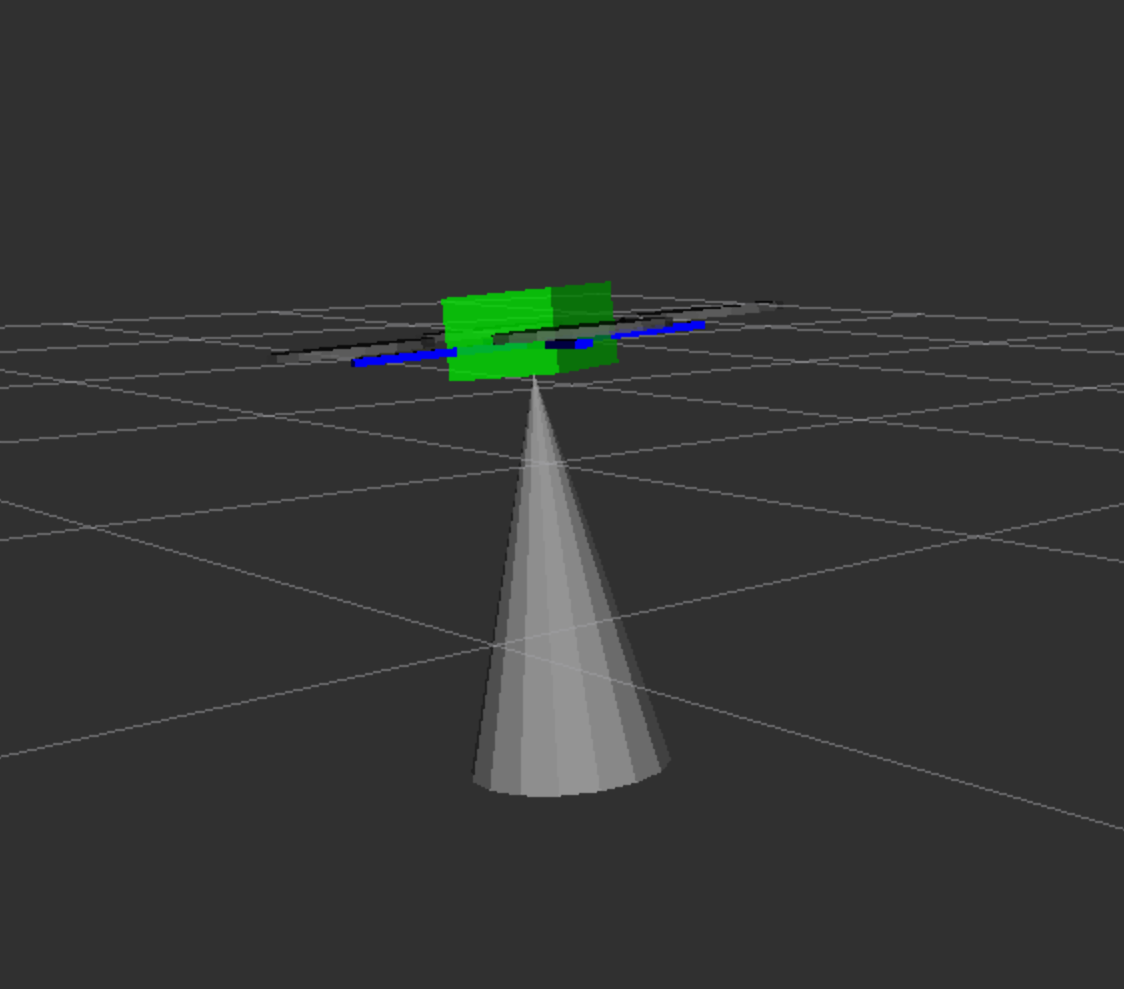
Read more about rviz and rqt.